SUBJECTS
GRADE
Show Results
Introduction to Scarborough Fair
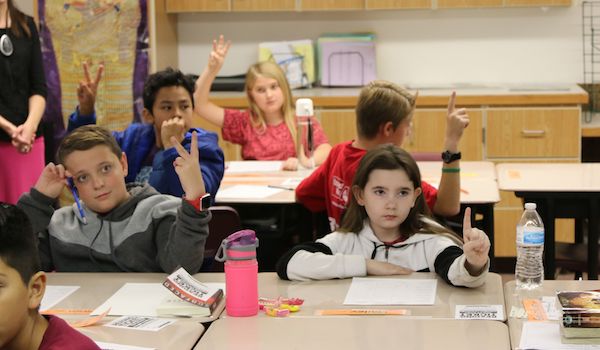
Lesson Summary
- Gain insight into the Renaissance period.
- Compare and contrast three versions of “Scarborough Fair.”
Lesson Plan and Procedure
Lesson Key Facts
- Grade(s): 6
- Subject(s): English Language Arts, Music, Social Studies
- Duration of lesson: 45 minutes
- Author(s): Emily Soderborg
Listening and Responding
Begin the lesson by asking students the following questions:
- What is your favorite song?
- Do you know if there are other recordings of the song?
- How old is the song?
Teacher: We are going to listen to a song today that some of you may have heard before, but it might be new to others. As you listen, see if you can find the beat. You may tap to find the beat, but do so without making noise. After you find the beat, see if you can find the strong and weak pattern within the beats to figure out what the time signature is. The pattern could be strong-weak (two meter), strong-weak-weak (three meter), or strong-weak-weak-weak (four meter).
Have students listen to the Simon and Garfunkel recording of “Scarborough Fair.”
Teacher: What strong-weak pattern best fits with the song? Yes, the strong-weak-weak pattern fits, which means the time signature is 3/4. Did any of you recognize the song? Besides the time signature, what else did you notice about it?
This is an introductory lesson; the questions asked are to see what students hear in their first listening. Whatever responses they give provide a basis to build on later  and help the teacher know what to focus on when they hear the song in the future.
and help the teacher know what to focus on when they hear the song in the future.
Teacher: Let’s sing the melody. Instead of singing the lyrics, we’ll sing “loo” for each of the syllables in the lyrics. Let’s see how much we can remember of the melody.
Listen to the first verse of the Simon and Garfunkel recording again if the students need help remembering the melody.
Teacher: We figured out that the time signature is three meter. We are going to use that pattern to help us play a simple rhythm on hand drums (or just on their hands).
Direct the students to hold the hand drum with their non-dominant hand. With the other hand, they should play the strong beat in the center of the drum (or tap the palm of their hand) and the weak beats on the rim or edge of the drum (or brush the heel of their hand). Have them practice playing this pattern while singing the melody on “loo” again.
As a challenge for students, have them figure out the pattern of the chimes in the recording. This could be done using any melodic instrument, but tone bells, glockenspiels, or soprano xylophones would work especially well. Have the students figure out the melodic pattern out by ear as they listen carefully to the recording. (For the teacher’s benefit, the notes are G, E, F#, and D in the key of E minor, or mi, do, re, and ti in solfege.)
Analyze and Compare
Teacher: Simon and Garfunkel did not write “Scarborough Fair.” In fact, the song is so old that no one really knows who wrote it. It comes from the Renaissance period, which was from approximately 1450 to 1600. Today, we are going to listen to and compare three recordings of this song. We will listen again to the Simon and Garfunkel version, and then listen to the oldest known recorded version of this melody, from 1955. (Recording technology was invented in 1877 by Thomas Edison, but it was another 73 years before this specific song was recorded.) We will finish by listening to a newer version of the song, performed on TV in 2013. All of these recordings are close to the traditional style of the song that would have been sung in the Renaissance period.
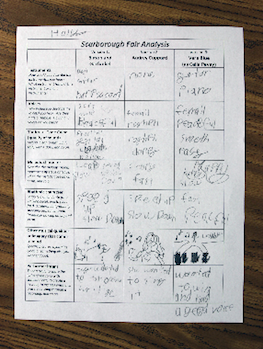 Pass out blank Scarborough Fair Analysis to each student.
Pass out blank Scarborough Fair Analysis to each student.
Teacher: Before we listen, let’s write down what we already know about the Simon and Garfunkel version. What instruments do you remember hearing? (Finger-picked guitar, chimes, harpsichord embellishments, recorder.)
Teacher: How would you describe the voices you heard? Were they male or female? How many voices did you hear? (Two male singers, singing in harmony.)
Teacher: Timbre and tone color are synonyms, and both of these terms describe the aspects of a musical sound that do not have anything to do with the melody or rhythm. What words would you use to describe the timbre? Here are some descriptive words you might consider: brassy, raspy, gentle, raucous, strong, eerie, choppy, mellow, shrill, reedy, clear, breathy, rounded, full, thin, piercing, harsh, warm, resonant, dark, bright, heavy, light, or flat. Do any of these words fit what you heard? Can you think of any other words?
Teacher: Here are some words you might use to describe the rhythmic character: largo (slow), adagio (slow and stately, or literally “at ease”), andante (at a walking pace), allegro (fast, quickly, and bright), presto (very fast), steady, following the rhythm of the breath, irregular, swung, dotted, repetitive, rubato (freely adjusting the tempo for expressive purposes), speech-like, uneven, hypnotic, continuous, distinct, iambic, anacrusic (with one or more unstressed syllables at the beginning), crusic (with the first syllable stressed), accelerando (gradually speeding up), or rallentando (gradually slowing down). Which of these do you think fit the piece? Are there other words you could use to describe the music?
Teacher: How would you describe the melody? How would you describe the mood of the music? (Is it major or minor?) Do the individual notes in the melody move more by steps or leaps? Steps are notes right next to each other, like walking up or down stairs. Leaps in the melody would be like jumping over several stairs to get to a much higher or much lower note without all the notes in between. When does the melody go up and when does it go down? How else could you describe it?
 Teacher: Did any images come to your mind as you listened to the music? What do you think the performers’ intent was in performing this song?
Teacher: Did any images come to your mind as you listened to the music? What do you think the performers’ intent was in performing this song?
Some possible performers’ intentions could be to entertain, to share the lyrics of the song with someone else, to create a new hit, to express their own emotions, and so on. All responses should be appreciated.
Teacher: As we listen to the Simon and Garfunkel version again, see if you hear anything else that you can add to what you have already written on your analysis form. Listen and write without talking to your neighbor.
Listen to all three pieces again. Have students work alone for a few minutes, then in partners or small groups, and finally discuss answers with the entire class.
Teacher: What do you think makes a song, such as “Scarborough Fair,” last through the ages? It was popular hundreds of years ago and is still being performed today. Do you think there is music being written now that will still be popular in 500 years? Out of the three versions you heard today, show me with your fingers which was your favorite. Hold up one finger for version 1, two fingers for version 2, or three fingers for version 3.
 Wrap up the lesson with students watching Paul Simon sing “Scarborough Fair” with the Muppets. Point out the actual features of the Renaissance period (e.g., lute, fair, maypole) displayed in the video.
Wrap up the lesson with students watching Paul Simon sing “Scarborough Fair” with the Muppets. Point out the actual features of the Renaissance period (e.g., lute, fair, maypole) displayed in the video.
Ask students to think about what the song might mean. Let them know that they will talk about the meaning of the song in the next lesson.
Assessment
- Students can tell the time signature for “Scarborough Fair” (three meter).
- Students can play short patterns on instruments.
- Students can sing the melody of “Scarborough Fair.”
- Students can compare three different versions of “Scarborough Fair.”
- Students can give their opinions of why they think “Scarborough Fair” has lasted for over 500 years.
Learning Objectives
- Gain insight into the Renaissance period through experiences with the song “Scarborough Fair.”
- Sing a traditional song in tune.
- Listen for and identify form, meter, rhythm, timbre, dynamics, tempo, melody, texture, and harmony/tonality.
- Experience and explore music which connects us to history, culture, and heritage.
- Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly.
Utah State Board of Education Standards
This lesson can be used to meet standards in many grades and subject areas. We will highlight one grade’s standards to give an example of application.
Grade 6 Social Studies
Standard 6.1.4: Identify some of the economic systems and technologies (for example, irrigation, writing systems, farming techniques, trading and bartering, coins and currency) created by civilizations found in different regions of the world, and categorize how they met specific human needs or wants.
Standard 6.1.5: Compare the cultures of civilizations found in different regions of the world and identify examples of cultural expression (for example, architecture, writing, philosophy, artwork).
- Strand 2: Globalization - Students will compare how the transformation and changes of the post-classical era (Ca. 500 C.E.–1500 C.E.) set in motion the expansion of knowledge through science, language, writing, religion, and technological innovations. They will understand how this created and encouraged a global interconnectedness among distant societies and civilizations that ripples into modern history.
Grade 6 Music
- Standard 6.M.P.4: Sing folk, traditional, and rounds in tune, with good vocal tone and clear diction.
- Standard 6.M.P.7: Perform and identify rhythm patterns in two-, three-, four-, and six-beat meters using body percussion, voice, and simple instruments.
- Standard 6.M.R.1: Listen to and interact with a variety of contrasting music.
- Standard 6.M.R.2: Listen for and identify form, meter, rhythm, timbre, dynamics, tempo, melody, texture, and harmony/tonality.
- Standard 6.M.R.4: Describe feelings or imagery conveyed by a music selection.
- Standard 6.M.R.5: Identify possible intent of a music selection, and how the music elements are used to convey it.
- Standard 6.M.CO.2: Draw upon interests, knowledge, and skills developed to inspire and inform the creation, performance, and appreciation of music, and deepen understanding of another content area through music.
- Standard 6.M.CO.3: Experience and explore music which connects us to history, culture, heritage, and community; identify connections between a music genre and cultural or historical contexts; and explore and explain how musical works are influenced by a composer’s heritage and experiences.
Grade 6 English Language Arts
Standard 6.SL.1: Participate effectively in a range of conversations and collaborations on topics, texts, and issues.
Respectfully acknowledge comments, claims, and evidence from multiple perspectives and identify contradictions when applicable.
Participate in conversations by posing questions, acknowledging new information, qualifying or justifying responses with reasoning and elaboration, and keeping the discussion on topic.
Equipment and Materials Needed
- Audio recordings of “Scarborough Fair”
- Simon and Garfunkel: Simon, P. & Garfunkel, A. (performers). (1999). Scarborough fair/ canticle. On The best of Simon and Garfunkel [iTunes]. New York, NY: Sony Music Entertainment Inc. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-BakWVXHSug
- Audrey Coppard: Coppard, A. (performer). (1956). Scarborough fair. On English folk songs [iTunes]. New York, NY: Folkways Records. https://folkways.si.edu/audrey-coppard/scarborough-fair/celtic-world/music/track/smithsonian
- The Voice [Australia], Celia Pavey [later known as Vera Blue] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lUbiDYhGpHQ
- Pavey, C. (performer). (2013). Scarborough fair. On This Music [YouTube]. Sydney, Australia: Universal Music.
- Instruments:
- Hand drums (optional)
- Melodic instruments (tone bells, glockenspiels, or soprano xylophones)
- Scarborough Fair Analysis
- Video recording
- The Muppet Show, Episode 511, “Scarborough Fair,” featuring Paul Simon: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dCcKIPbQiHY
Additional Resources
- This is the first of several lessons in a unit focused around the song “Scarborough Fair.” They introduce various aspects of the Renaissance period. The other lessons in the unit include the following:
- The following book has an entire chapter filled with lesson plans and ideas devoted to teaching the Renaissance using integrated curriculum:
- Barrett, J., McCoy, C., & Veblen, K. (1997). Sound Ways of Knowing. New York, NY: Schirmer Books.
- Renaissance music lesson plans: https://study.com/academy/topic/renaissance-music-lesson-plans.html
Image References
Images 1–5: James Houston.

www.education.byu.edu/arts/lessons
 Download
Download